This guide is designed to help you style our default Universal Checkout UI. If you would like to build your own UI from scratch then check out our Headless Universal Checkout guide.
Localization and languages
Set the locale
Universal Checkout supports multiple languages out of the box, enabling you to adapt its UI to the relevant market.
You can specify the language using the locale option. If not provided, the locale is automatically derived from the browser:
const options = {
/* Other checkout options ... */
locale: 'fr-FR', // Renders Universal Checkout in French
}
Universal Checkout automatically falls back to English if the provided locale is not supported.
Supported locales
| Locale | Language | Minimum versions |
|---|
| ar | Arabic | v1.22.1 |
| bg-BG | Bulgarian (Bulgaria) | v2.1.1, v1.37.0 |
| cs-CZ | Czech (Czech Republic) | v2.3.0, v1.38.0 |
| da-DA | Danish | v1.22.1 |
| de-DE | German | v1.22.0 |
| el-GR | Greek (Greece) | v1.22.1 |
| en-US | English (United States) | v1.0.0 |
| es | Spanish | v1.22.0 |
| es-AR | Spanish (Argentina) | v2.2.1 |
| et-EE | Estonian (Estonia) | v2.3.0, v1.38.0 |
| fr-FR | French (France) | v1.19.0 |
| hr-HR | Croatian (Croatia) | v2.3.0, v1.38.0 |
| hu-HU | Hungarian (Hungary) | v1.18.0 |
| it-IT | Italian (Italy) | v2.1.1, v1.37.0 |
| ja-JP | Japanese (Japan) | v2.3.0, v1.38.0 |
| lt-LT | Lithuanian (Lithuania) | v2.3.0, v1.38.0 |
| ms | Malay | v2.26.1 |
| nb-NO | Norwegian (Norway) | v1.22.1 |
| nl-NL | Dutch (Netherlands) | v1.22.1 |
| pl-PL | Polish (Poland) | v1.22.1 |
| pt-BR | Portuguese (Brazil) | v2.3.0, v1.38.0 |
| pt-PT | Portuguese (Portugal) | v1.22.0 |
| ro-RO | Romanian (Romania) | v1.37.0 |
| ru-RU | Russian (Russia) | v2.1.1, v1.37.0 |
| sk-SK | Slovak (Slovakia) | v2.1.1, v1.37.0 |
| sv-SE | Swedish (Sweden) | v1.22.1 |
| th | Thai | v2.26.1 |
| tr-TR | Turkish (Turkey) | v1.22.1 |
| vi-VN | Vietnamese (Vietnam) | v2.3.0, v1.38.0 |
| zh-CN | Chinese (Mainland China - Simplified characters) | v2.26.1 |
| zh-HK | [BETA] Chinese (Hong-Kong - Traditional characters) | v2.26.1 |
| zh-TW | [BETA] Chinese (Taiwan - Traditional characters) | v2.26.1 |
Right-to-left
Universal Checkout automatically switches to a right-to-left layout for the relevant languages.
Make sure to pass the right locale to activate right-to-left:
const options = {
/* Other checkout options ... */
locale: 'ar-AR', // Renders Universal Checkout in Arabic with right-to-left layout
}
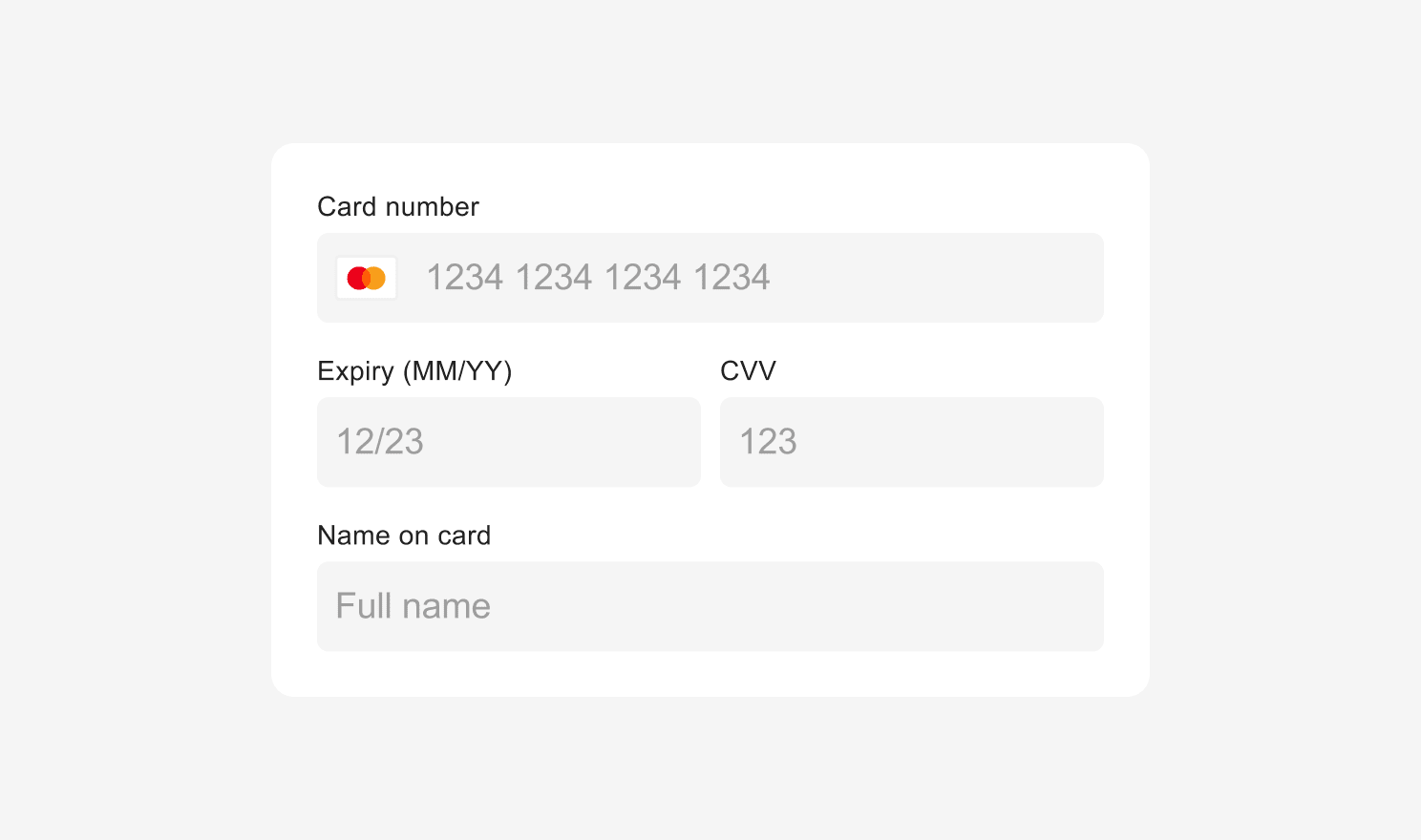
Styling Universal Checkout
For styling Universal Checkout, do not use custom CSS. Rather pass the style object as a checkout option when calling showUniversalCheckout.
const options = {
/* Other checkout options ... */
style: {
/* Style options */
},
}
Text Styling Options
Text elements within Universal Checkout can be styled using the following interface:
interface TextStyle {
color?: string
fontFamily?: string
fontWeight?: string
fontSize?: string
fontSmoothing?: string
lineHeight?: string
textTransform?: string
letterSpacing?: string
}
Block Styling Options
Block elements within Universal Checkout can be styled using the following interface:
interface BlockStyle {
background?: string
borderRadius?: number | string
boxShadow?: string
borderStyle?: string
borderColor?: number | string
borderWidth?: number | string
}
Both of the above mentioned interfaces will be referred to regularly in this guide when covering the styling of specific UI elements.
iframe.
So any font-family that you have set in the CSS file will be used by the Universal Checkout. The example below uses MyFont as the preferred font family for card input.
#my-checkout {
font-family: 'MyFont', sans-serif;
}
iframe. This means that font-family declarations, and @font-face directives that load and define fonts are not passed to these specific fields.
To forward font-family and @font-face to the card input fields, you can set style.input.base.fontFamily and style.fontFaces.
Alternatively, to style.fontFaces, you can forward stylesheets to the iframe using the style.stylesheets option, which facilitates the integration of fonts coming from services such as Google Fonts.
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
/* Forwarded to iframes */
fontFaces: [
{
fontFamily: 'Open Sans',
src: 'url("/fonts/OpenSans-Regular-webfont.woff2") format("woff2"), url("/fonts/OpenSans-Regular-webfont.woff") format("woff")',
},
],
/* Forwarded to iframes */
stylesheets: [
{
href: '<https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Roboto:wght@100&display=swap>',
},
],
/* Unified across all inputs: inside and outside iframes */
input: {
base: {
fontFamily: 'Open Sans',
},
},
},
}
InputStyle defined in input:base will be used everywhere. You need to add value for InputStyle only if you wish to override this style for inputLabel, hover, placeholder etc.
interface InputStyle {
height?: number
paddingHorizontal?: number
background?: string
borderRadius?: number | string
boxShadow?: string
borderStyle?: string
borderColor?: string
borderWidth?: number | string
color?: string
fontFamily?: string
fontWeight?: string
fontSize?: string
fontSmoothing?: string
lineHeight?: string
}
interface CheckoutStyle {
// Input styling
input?: {
// Base style
base?: InputStyle & {
hover?: InputStyle // :hover
focus?: InputStyle // :focus
placeholder?: InputStyle // ::placeholder
webkitAutofill?: InputStyle // :-webkit-autofill
selection?: InputStyle // ::selection
}
// Style of the label displayed above the input fields
inputLabel?: TextStyle
}
}
Example
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
inputLabel: {
fontFamily: 'courier new',
color: '#000000',
},
input: {
base: {
borderStyle: 'none none solid none',
borderColor: '#000000',
boxShadow: '0px',
background: '#ffffff',
fontFamily: 'courier new',
borderRadius: '0px',
paddingHorizontal: '0px',
lineHeight: '',
color: '#000000',
placeholder: {
color: '#e1deda',
},
},
},
},
}
You can hide the default input labels using the inputLabelsVisible option.
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
form: {
inputLabelsVisible: false,
},
}
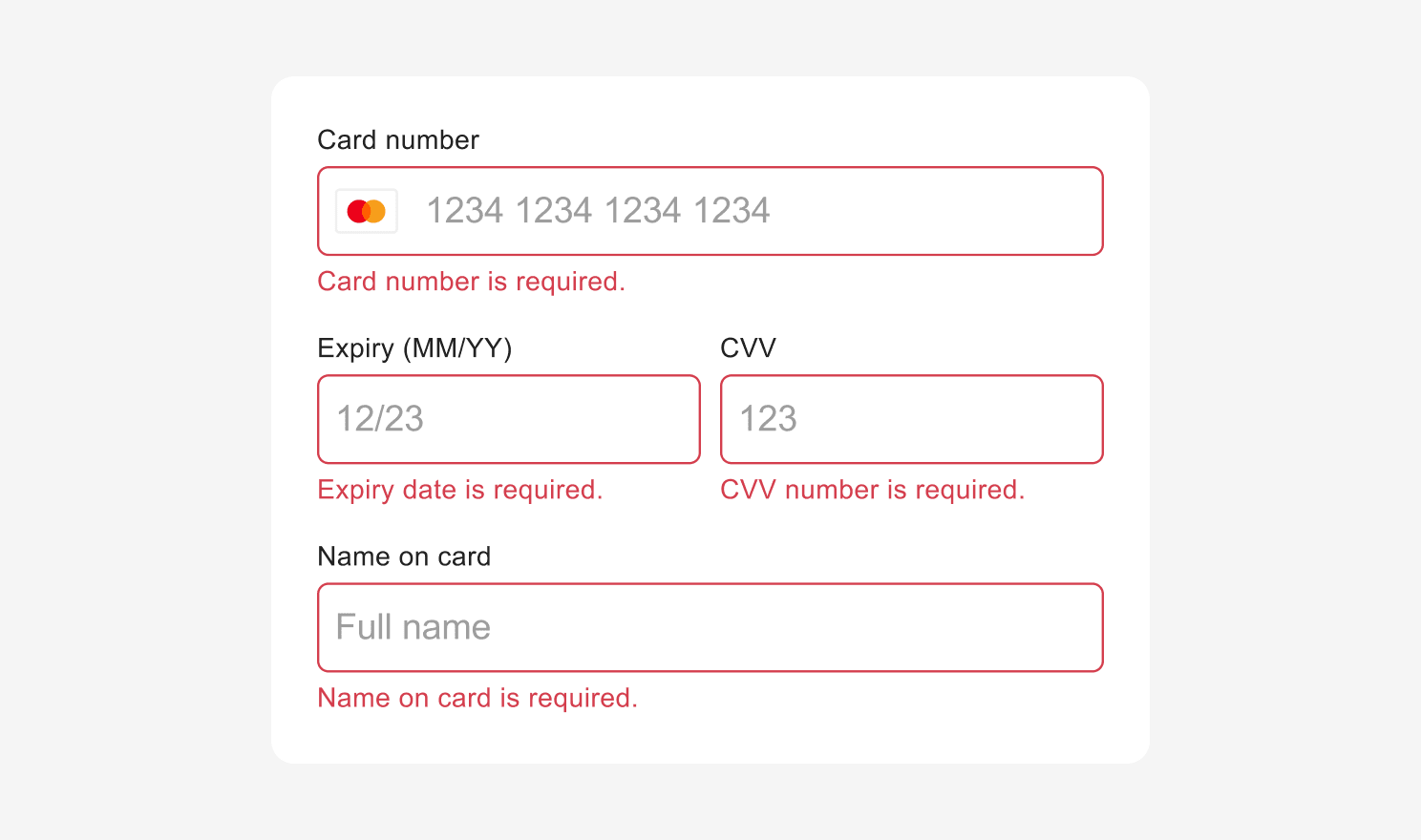
InputStyle defined in input.base will be used everywhere. But you can override this where you need different error message styling by specifying the style for input.error and inputErrorText. inputErrorText also uses TextAlignmentStyle.
interface TextAlignmentStyle {
textAlign?: string
}
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
input: {
error:
InputStyle &
{
hover: InputStyle,
focus: InputStyle,
placeholder: InputStyle,
webkitAutofill: InputStyle,
selection: InputStyle,
},
},
// Style of the error messages displayed below the input fields
inputErrorText: TextStyle & TextAlignmentStyle,
},
}
Example
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
inputErrorText: {
fontFamily: 'courier new',
textAlign: 'left',
color: '#e70909',
},
inputLabel: {
fontFamily: 'courier new',
color: '#000000',
},
input: {
base: {
borderStyle: 'none none solid none',
borderColor: '#000000',
boxShadow: '0px',
background: '#ffffff',
fontFamily: 'courier new',
borderRadius: '0px',
paddingHorizontal: '0px',
lineHeight: '',
color: '#000000',
placeholder: {
color: '#e1deda',
},
error: {
borderStyle: 'solid',
borderColor: '#d0021b',
},
},
},
},
}
Styling Error Messages
You can also style the error message shown in the event of an unsuccessful payment using ErrorMessageStyle interface which extends Block Styling Options and Text Styling Options mentioned above.
// Error Message Interface
interface ErrorMessageStyle extends BlockStyle, TextStyle {
color?: string
}
// Example
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
errorMessage: ErrorMessageStyle,
},
}
formSpacings properties.
// Form Spacings Interface
interface FormSpacings {
betweenLabelAndInput?: string
betweenInputs?: string
}
// Example
const options = {
style: {
formSpacings: {
betweenLabelAndInput: '0px',
betweenInputs: '10px',
},
},
}
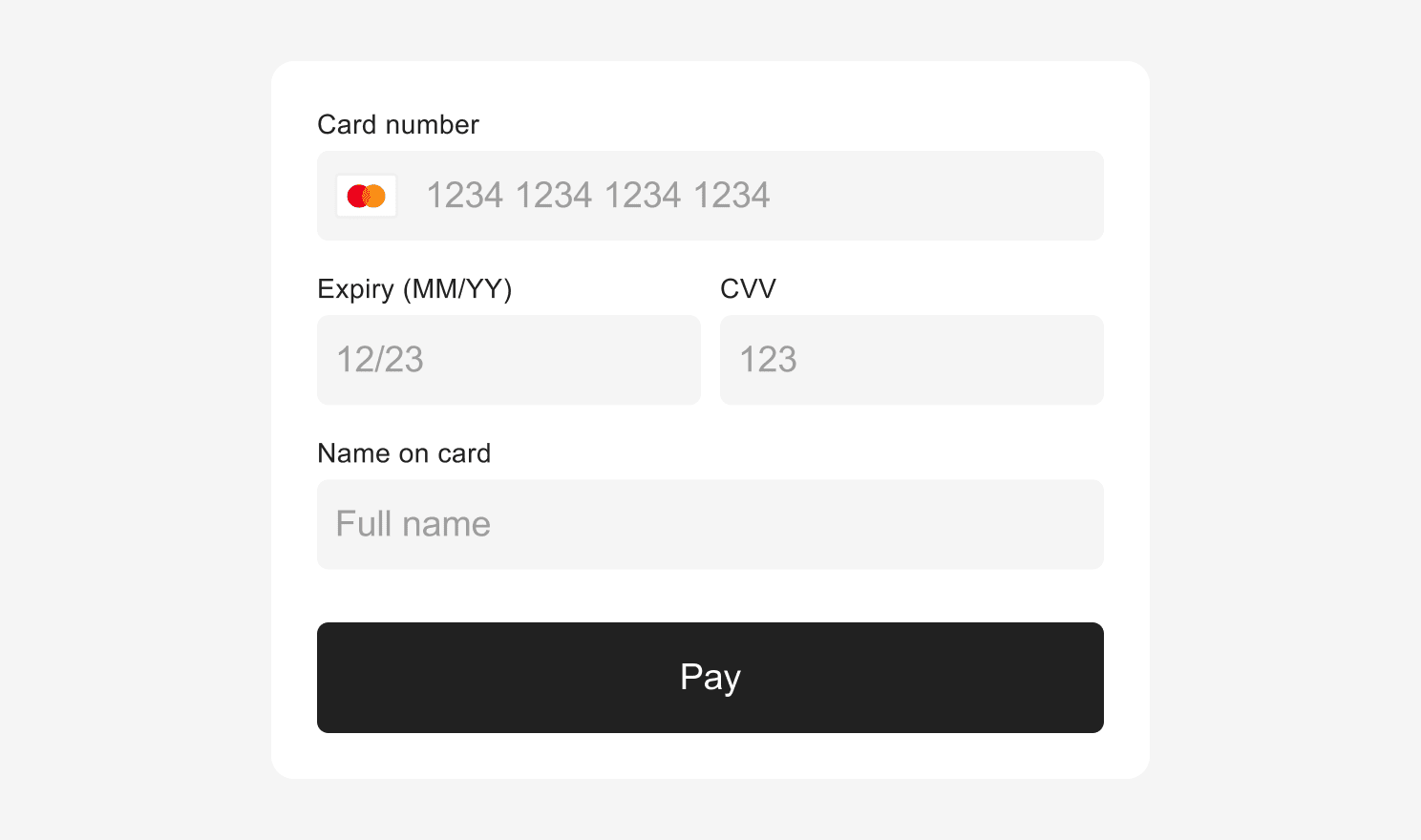
submitButton uses TextStyle and BlockStyle to define the style of the button.
By default, the style defined in submitButton.base will be used everywhere. If you wish to override the default style for loading, disabled, hover or focus or other states, you will be required to add values for TextStyle and BlockStyle properties.
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
submitButton: {
base: {
hover: TextStyle & BlockStyle,
focus: TextStyle & BlockStyle,
},
disabled: {
hover: TextStyle & BlockStyle,
focus: TextStyle & BlockStyle,
},
loading: {
hover: TextStyle & BlockStyle,
focus: TextStyle & BlockStyle,
},
},
},
}
Example
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
submitButton: {
base: {
color: '#ffffff',
background: '#000000',
borderRadius: '3px',
fontFamily: 'courier new',
fontWeight: 'bold',
boxShadow: 'none',
},
disabled: {
color: '#9b9b9b',
background: '#e1deda',
},
},
},
}
You can also use custom submit button instead of styling the Universal Checkout default submit button. const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
backButton: {
color: string,
},
},
}
Styling Transitions
When multiple scenes are present in Universal Checkout, you can override the default transitions to better match your website transitions.
type SceneOptions = {
// A callback for receiving the current scene that is entering
onEntering?: (sceneId: string) => void
// Specify options relating to scene transitions
// Setting to false disables all scene transitions
// Defaults to a 'SLIDE_UP' type transition with a duration of 700ms
transition?: SceneTransitionOptions | false
}
type SceneTransitionOptions = {
// The type of transition animation which will be used
type: TransitionType
// The duration of the transition animation
duration: number
}
type TransitionType = 'SLIDE_UP' | 'SLIDE_DOWN' | 'SLIDE_HORIZONTAL'
const handleOnSceneEntering = (sceneId: string) => {
// perform action based on current scene being entered
}
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
// Example 1 - scene with custom transitions enabled
scene: {
onEntering: handleOnSceneEntering,
transition: {
type: 'SLIDE_DOWN',
duration: 650, // duration in milliseconds
},
},
// Example 2 - scene with all transitions disabled
scene: {
onEntering: handleOnSceneEntering,
transition: false,
},
}
Styling Loading indicator
While Universal Checkout loads, a loading screen indicator is displayed to the customers. You can customize the color of the loading screen indicator as shown below:
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
loadingScreen: {
// Color of the loading screen indicator
color: string,
},
},
}
Styling Vault
By default, any previously vaulted payment methods are shown to customers in Universal Checkout. This happens only when the customerId is included in the client session.
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
vault: {
// Fetch the vaulted payment methods for the customerId
//of the current session and display them
// Default to true
visible: boolean,
// Disable the option to delete a saved payment method.
// Default to false
deletionDisabled: boolean,
},
}
Styling Vault Display
The vault display in Universal Checkout can be styled if you wish to change the defaults. showMorePaymentMethodsButton uses TextStyle to define the style of the button. By default, the style defined in showMorePaymentMethodsButton.base will be used everywhere. Add values for TextStyle only if you wish to override this style for the disabled state.
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
showMorePaymentMethodsButton: {
base: TextStyle,
disabled: TextStyle,
},
},
}
actionButton uses TextStyle to define the style of the button. The confirmButton uses both TextStyle and BlockStyle interfaces.
// Pop-up menu to manage the vaulted payment methods
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
// Pop-up menu to manage the vaulted payment methods
vaultMenu: {
// Pencil icon
editButton: {
// Backround of the pencil icon
background: string,
// Color of the pencil icon
color: string,
},
item: {
label: textStyle,
// Delete & Cancel button
actionButton: TextStyle,
confirmButton: TextStyle & BlockStyle,
},
},
}
Displaying Custom Errors
In case of an error, Universal Checkout presents a default message to the customers. This error message can be disabled if you wish to display a custom error message.
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
errorMessage: {
// Disable the appearance of the
//default error message
// Default to false
disabled: boolean,
// A callback for when the error message
//should be displayed
onErrorMessageShow(message: string) {
// Choose to use provided message for own purposes
},
// A callback for when the error message
//should be hidden
onErrorMessageHide() {
// Update own UI accordingly
},
},
}
type CardPreferredFlow = 'DEDICATED_SCENE' | 'EMBEDDED_IN_HOME'
// Example
Primer.showUniversalCheckout(clientToken, {
// ...
card: {
preferredFlow: 'DEDICATED_SCENE', // Show the card form on a separate scene
},
})
card.preferredFlow field:
DEDICATED_SCENEEMBEDDED_IN_HOME (default)
The style of the card form in the second dedicated scene remains defined by the style.input property. The pay with card button can also be styled, if you prefer not to use the default styling. See Styling Payment Method Button for details.
The paymentMethodButton uses TextStyle to define the style of the button.
const options = {
/* Other options ... */
style: {
paymentMethodButton: {
background: string,
borderRadius: number | string,
boxShadow: string,
borderColor: string,
height: number,
primaryText: TextStyle,
logoColor: logoColor,
marginTop: string,
},
},
}
const checkout = await primer.showUniversalCheckout(clientToken, {
submitButton: {
useBuiltInButton: false, // Hide the built-in submit button
},
})
Step 2. Forward clicks to checkout.submit()
const checkout = await primer.showUniversalCheckout(clientToken, options)
const handleMySubmitButtonClick = e => {
checkout.submit()
}
const checkout = await primer.showUniversalCheckout(clientToken, {
/* Other options ... */
submitButton: {
useBuiltInButton: false, // Hide the built-in submit button
// The Universal Checkout expects the button to be showed or hidden
onVisible: (isVisible: boolean) => {
// Show / Hide the submit button
},
// The Universal Checkout expects the button to be enabled or disabled
onDisable: (isDisabled: boolean) => {
// Enable / Disable the submit button
},
// The Universal Checkout expects the button to have a loading indicator
// to indicate that it is processing/loading something
// "isLoading: true" also means that the button is disabled
onLoading: (isLoading: boolean) => {
// Set the submit button to loading or not
},
// Set the content of your submit button
onContentChange: (content: string) => {
// Set the text content of the submit button
},
},
})
These callback functions are called every time the scene changes.
context with the currentSceneId. This enables you to determine which submit button to show/hide, enable/disable, or modify the content.
In addition, the onVisible callback also contains previousSceneId in the context object. This enables you to hide the button of the previous scene if necessary.
const getSubmitButtonFromSceneId = (sceneId: string) => {
if (sceneId === 'UniversalCheckout/Home') {
return 'SideButton'
} else if (sceneId === '...') {
return 'TopButton'
}
return 'BottomButton'
}
const onVisible = (isVisible, context) => {
const { prevousSceneId, currentSceneId } = context
if (!isVisible) {
hideAllSubmitButtons()
} else {
hideSubmitButton(getSubmitButtonFromSceneId(previousSceneId))
showSubmitButton(getSubmitButtonFromSceneId(currentSceneId))
}
}
const onContentChange = (content, context) => {
const { currentSceneId } = context
setSubmitButtonContent(getSubmitButtonFromSceneId(currentSceneId), content)
}
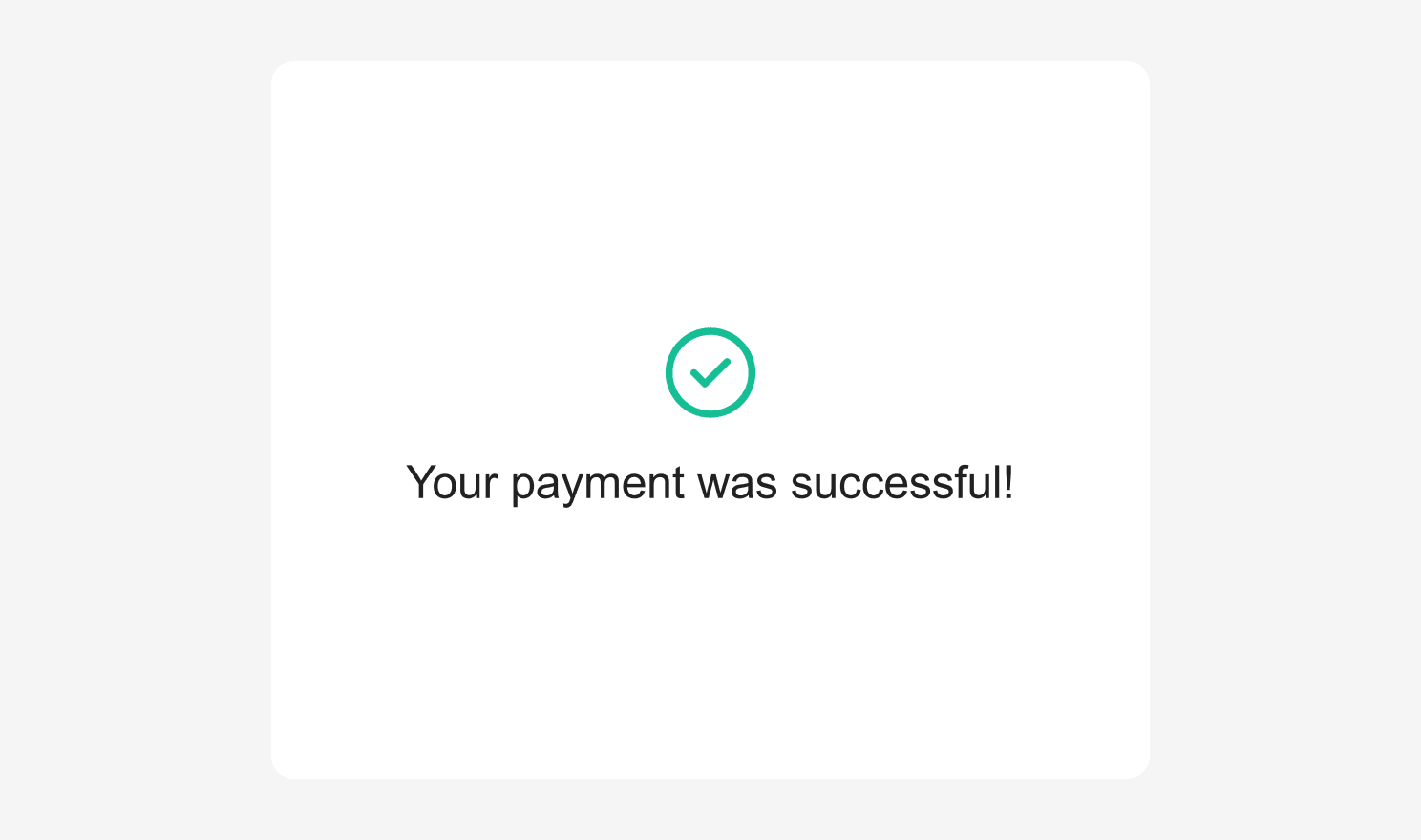
Success Screen
By default, what happens after onTokenizeSuccess depends on the payment method that the customer chooses. Some of them require the display of a screen that summarizes the order.
It is recommended best practice to show a success screen once the payment is validated. You can use the successScreen options to determine whether to show a built-in success screen or a custom one.
The available built-in success screen types are 'PAYMENT_METHOD' and 'CHECK'.
The default successScreen used when no type is defined is 'CHECK'.
Custom Title
When using 'CHECK' as a success screen type, it is also possible to specify a custom success title which will be displayed under the success check mark icon.
await primer.showUniversalCheckout(clientToken, {
/* Other options ... */
successScreen: {
type: 'CHECK',
title: 'My custom title',
},
})
successScreen to false overrides the default behavior so that you can show a custom success screen after onTokenizeSuccess is called:
await primer.showUniversalCheckout(clientToken, {
/* Other options ... */
successScreen: false,
})